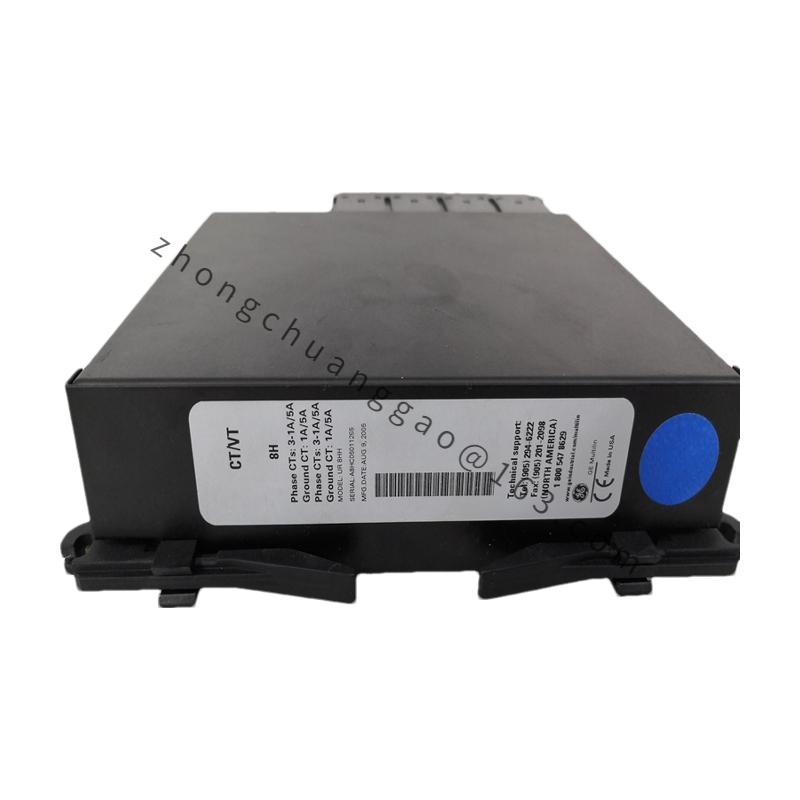
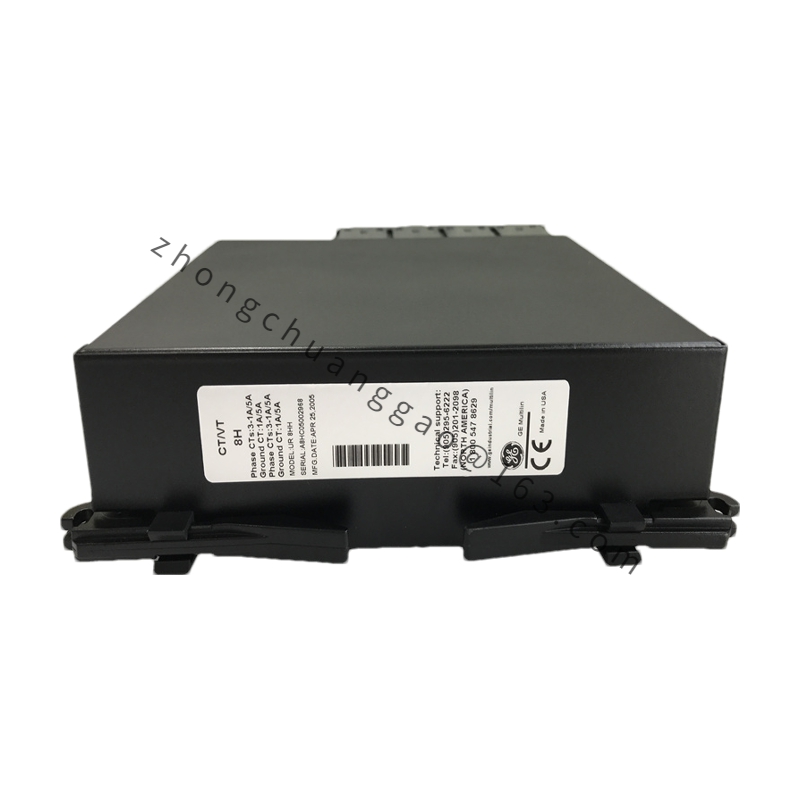
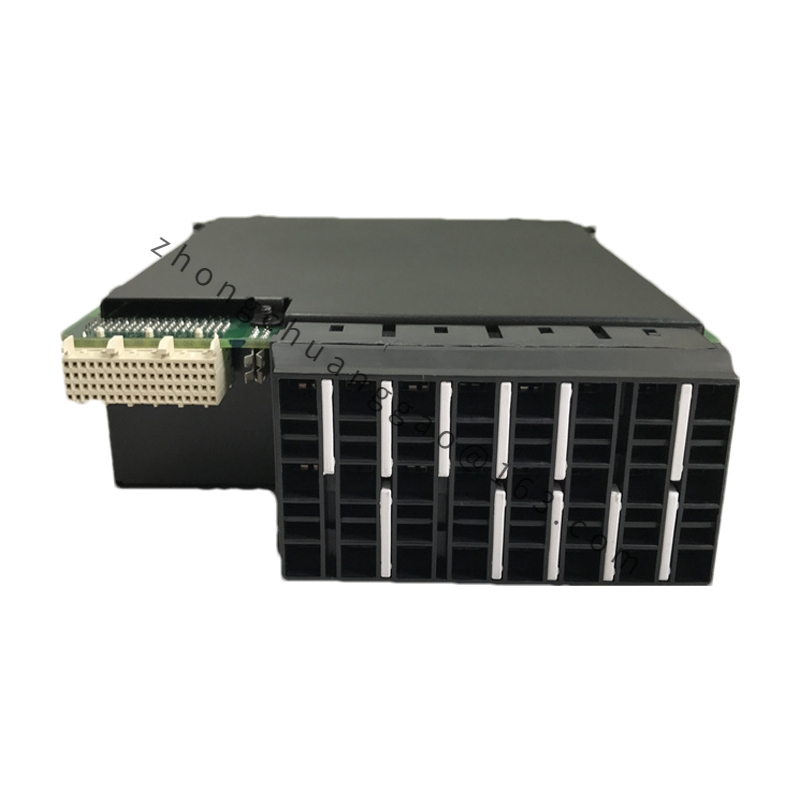
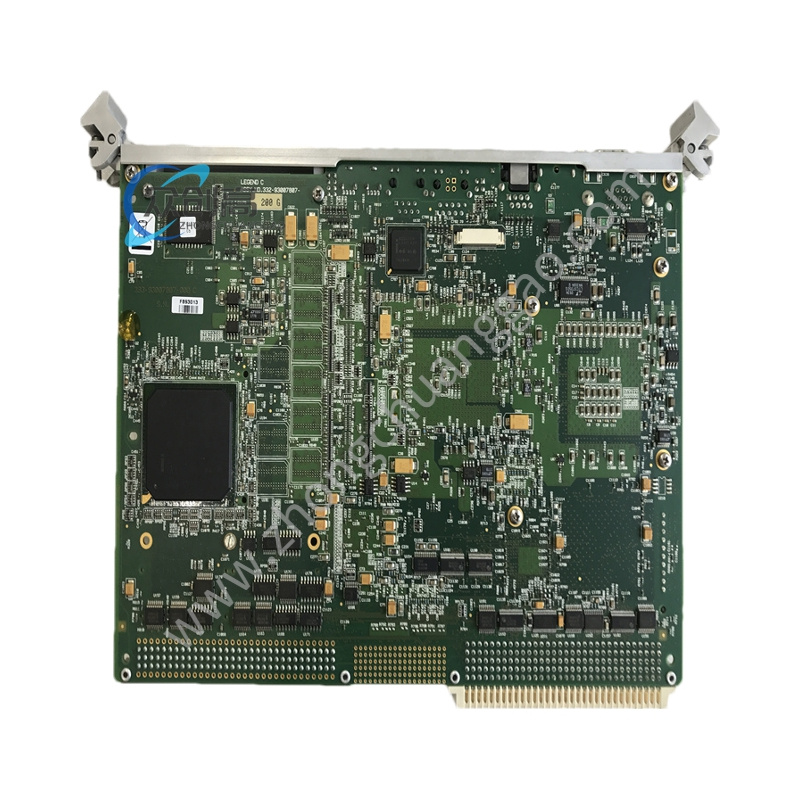
GE UR8HH
Technical Specifications
Type: Analog Input Module
Input Channels: Multiple analog input channels capable of receiving signals such as voltage or current.
Signal Conversion: Converts analog input signals into digital signals for further processing and control.
Input Types: Supports various analog input signals, including voltage, current, and potentially temperature.
Detailed content
Resolution: Offers different resolution options for varying levels of data acquisition precision.
Programmable Gain: Some models may feature programmable gain functionality, allowing users to adjust input signal gain as per application requirements.
Communication Interfaces: Equipped with communication interfaces like Ethernet or other industrial communication protocols for transmitting collected data to other devices or control systems.
Power Supply: Standard voltage input, details may vary depending on specific model and region.
Operating Temperature: Designed to operate within a wide temperature range suitable for industrial environments.
Functional Features
High Reliability: Designed for high reliability to meet the demands of industrial environments, ensuring stable and accurate data acquisition.
Alarm Function: Capable of setting thresholds and alarm conditions. Triggers alarms when input signals exceed set limits.
Data Storage: Some models may offer data storage capabilities, allowing for caching of collected data to prevent data loss.
Isolation: Provides isolation between analog input signals and digital outputs, enhancing system stability and reducing interference.
Flexibility: Supports different types of analog signals, making it versatile for various applications.
Configurable: Users can configure settings according to specific needs, including gain adjustments and alarm thresholds.
Application Scenarios
Industrial Automation Systems: Commonly used in industrial automation systems for data acquisition and monitoring. It is well-suited for monitoring process variables such as temperature, pressure, and flow rates.
Process Control: Ideal for process control applications where precise measurement and real-time monitoring of process variables are crucial.
Machinery Monitoring: Can be integrated into machinery monitoring systems to detect faults or deviations from normal operating conditions.
Power Generation and Distribution: Used in power generation and distribution networks for monitoring current, voltage, and other critical parameters.
Safety Systems: Plays a role in safety systems, providing critical data for early detection of potential hazards or failures.