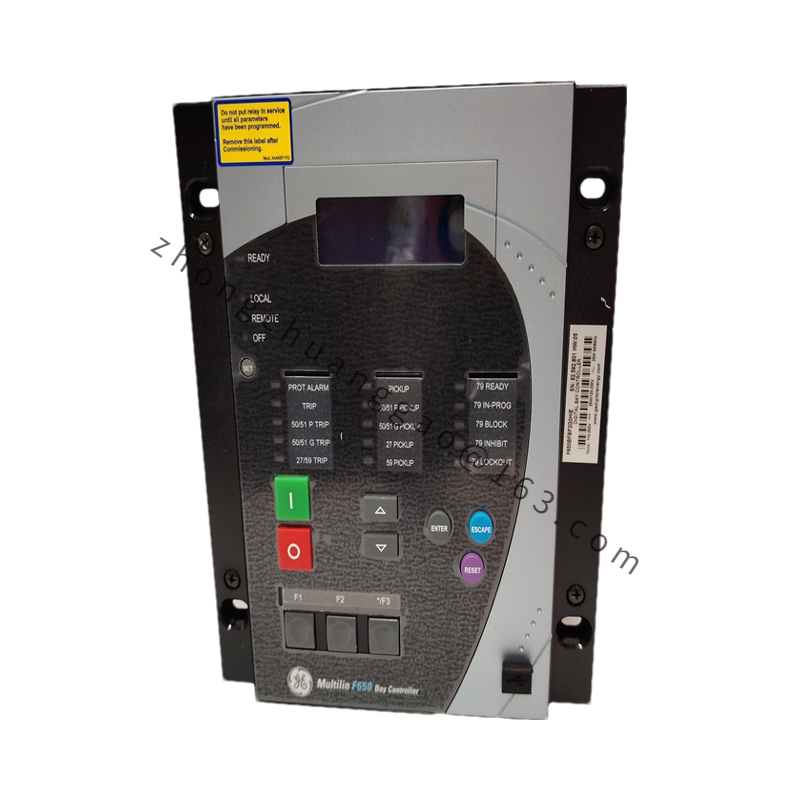
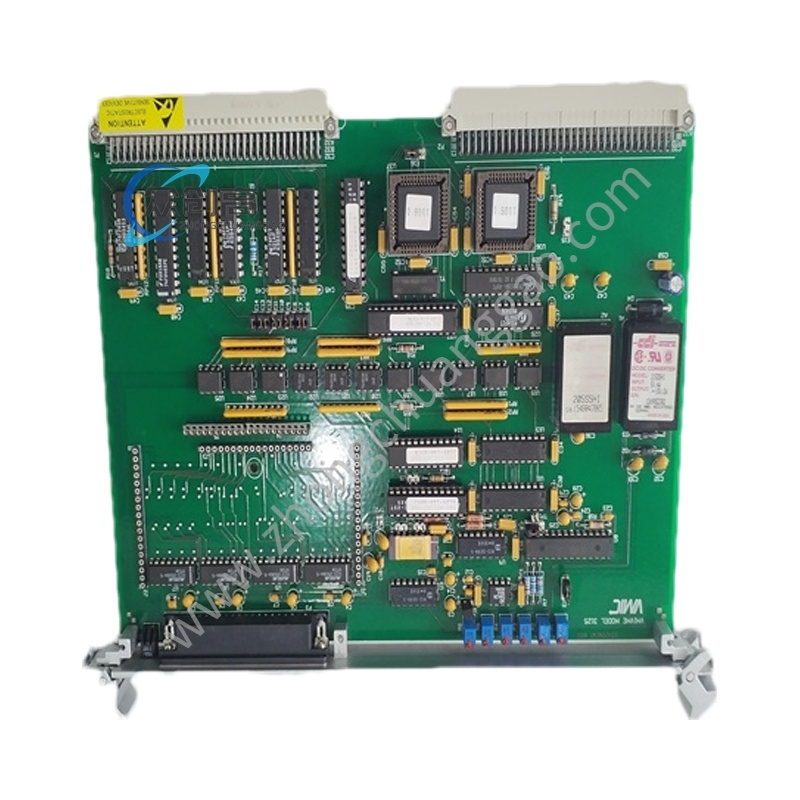
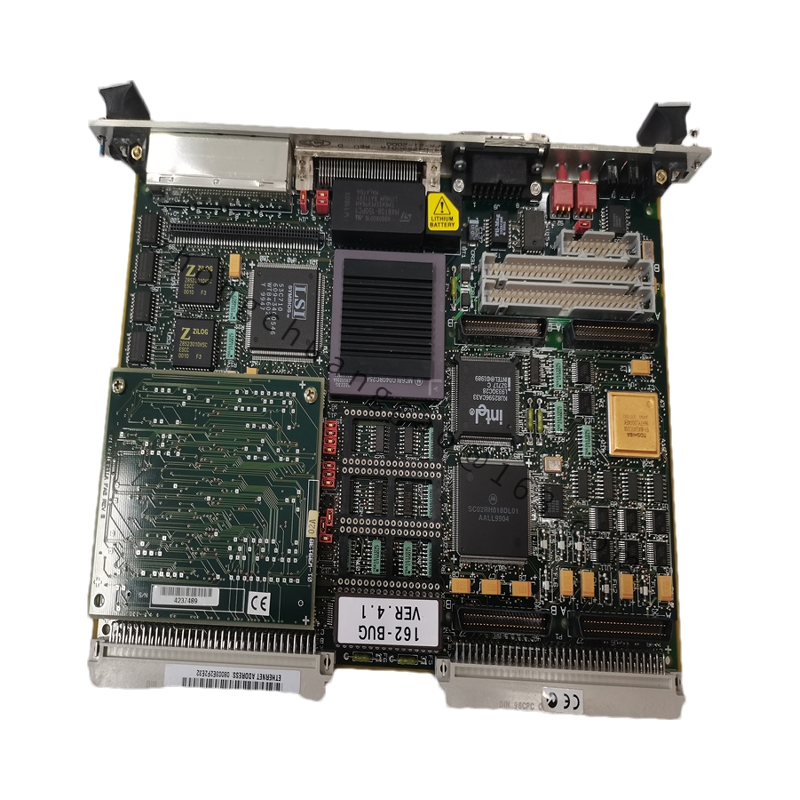
Detailed content
Technical Specifications:
- Processor Options:
- 32 MHz MC68040 enhanced 32-bit microprocessor with 8KB cache, MMU, and FPU.
- Optional 25 MHz MC68040 32-bit microprocessor with 8KB cache, MMU, and FPU.
- Optional 25 MHz MC68LC040 enhanced 32-bit microprocessor with 8KB cache and MMU.
- Bus Interface:
- A32/D64 VMEbus master/slave interface with system controller functionality.
- High-performance DMA support for VMEbus D64 and local bus memory burst cycles.
- Memory Configuration:
- Shared DRAM ranging from 4MB to 16MB, expandable with customer-installable memory modules.
- 512KB SRAM with battery backup.
- 1MB flash memory for on-board monitor/debugger or user-installed firmware.
- 8K x 8 NVRAM and clock with battery backup.
- Communication Interfaces:
- Two serial communication ports, with one console port as EIA-232-D DTE and the second port configurable for EIA-232-D/EIA-422 (V.36) DTE/DCE.
- Optional SCSI bus interface with 32-bit local bus burst DMA.
- Optional Ethernet transceiver interface with 32-bit local bus DMA.
- Industrial Connectivity:
- Up to four 16 or 32-bit IndustryPack® ports, each with a DMA channel, providing connections for various I/O, control, interface, analog, and digital functions.
Functional Characteristics:
- Scalability: The MVME162 offers scalability by allowing various MPU options, customizable clock speeds, and floating-point capabilities.
- Reliability: Designed for high reliability and stability, ensuring uninterrupted operation in demanding industrial environments.
- Connectivity: Supports multiple industrial communication protocols, facilitating seamless integration with other industrial devices.
- Ease of Maintenance and Upgrade: Provides diagnostic tools and functionalities for convenient troubleshooting and maintenance, along with the capability for upgrades and expansions as technology evolves.
Application Scenarios:
The GE MVME162 is an ideal choice for a wide range of industrial applications, including but not limited to:
- Industrial Automation: For controlling and monitoring various automated processes and machinery.
- Embedded Systems: As a core component in embedded systems requiring high-performance computing capabilities.
- CNC Machinery: Used in numerical control machines for precise motion control and data processing.
- Process Industries: In sectors such as metallurgy, oil and gas, petrochemicals, chemicals, paper and printing, textile dyeing, and electronics manufacturing, where reliability and precision are paramount.
- Infrastructure: Applicable in power, water, and wastewater treatment, as well as in municipal engineering projects.