Detailed content
Memory:
Battery-Supported Memory: 6MB
Non-Volatile User Flash Memory: 256K
I/O Capabilities:
Maximum Analog I/O: 8K
MaximumA Mixed I/O (Input/Output): 12K
Communication Interfaces:
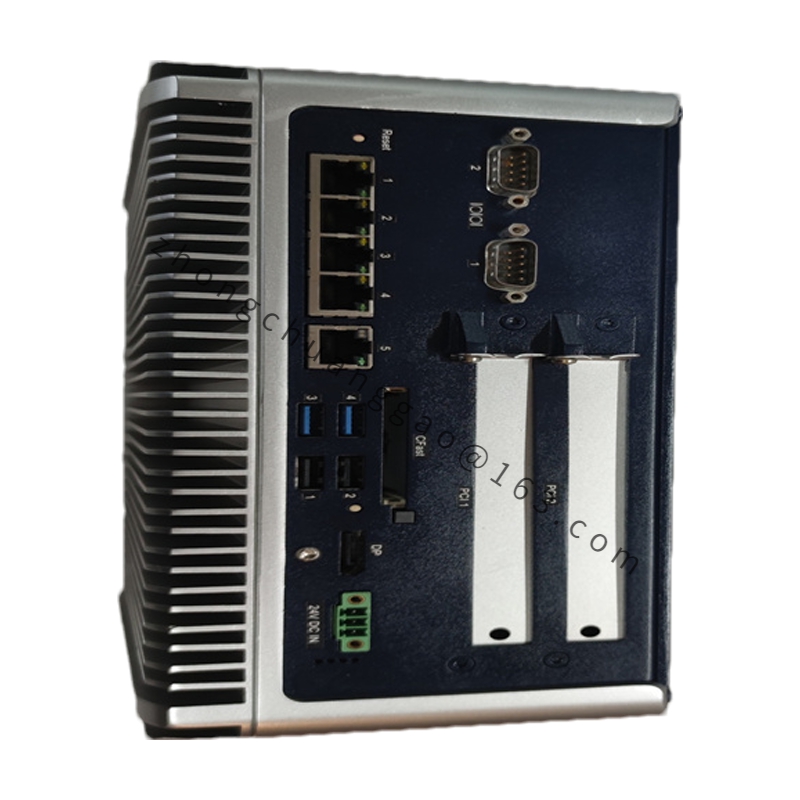
Serial Ports: 3 (RS-232, RS-485, and potentially others)
Ethernet
Other interfaces (depending on configuration and optional modules)
Physical Design: Single-slot design for easy installation in compatible racks
Functional Characteristics
High Processing Power: The 96MHz 80486DX4 microprocessor ensures fast execution of logic controls and algorithms, meeting the demands of high-performance industrial automation applications.
Versatile I/O: Supports up to 8K analog I/O and 12K mixed I/O, allowing for flexible integration with various sensors, actuators, and other control devices.
Comprehensive Communication: Provides multiple communication interfaces, including Ethernet and serial ports, enabling seamless data exchange with other devices and systems.
Expandability: Compatible with various optional modules, such as LAN Interface modules and programmable coprocessors, to extend and enhance the functionality of the CPU module.
Programming Flexibility: Supports MS-DOS or Windows-based software products, allowing for programming and configuration via Ethernet TCP/IP or through SNP ports.
Security and Stability: Incorporates security features like password-controlled access, remote programming key switch, and memory protection to ensure system security and stability.
Application Scenarios
Industrial Automation Systems:
Used to control and monitor equipment and machines in various manufacturing processes, improving productivity and efficiency.
Process Control Systems:
Deployed in industries like chemicals, oil, and gas to ensure stability and consistency in production processes.
Energy Industry:
Monitors and controls equipment and processes in power generation, distribution, and energy production facilities.
Manufacturing:
Controls machines, sensors, and other devices on production lines, enhancing overall production efficiency.
Transportation Systems:
Utilized in controlling and monitoring signals, sensors, and automated equipment in traffic systems, such as traffic light control.
Building Automation:
Integrates with building automation systems to control lighting, HVAC, and other building equipment, optimizing energy usage and comfort.
Data Acquisition and Monitoring:
Works with sensors and data acquisition devices to monitor environmental parameters and collect real-time data for analysis and decision-making.
Water and Wastewater Treatment:
Controls and monitors equipment in water treatment and wastewater treatment plants, ensuring efficient and safe operation.