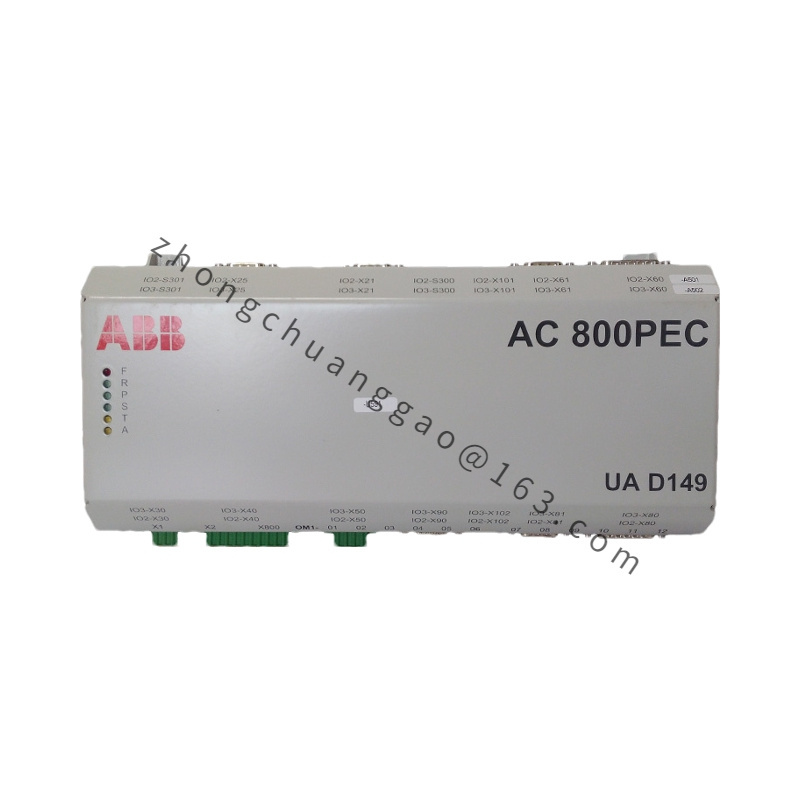
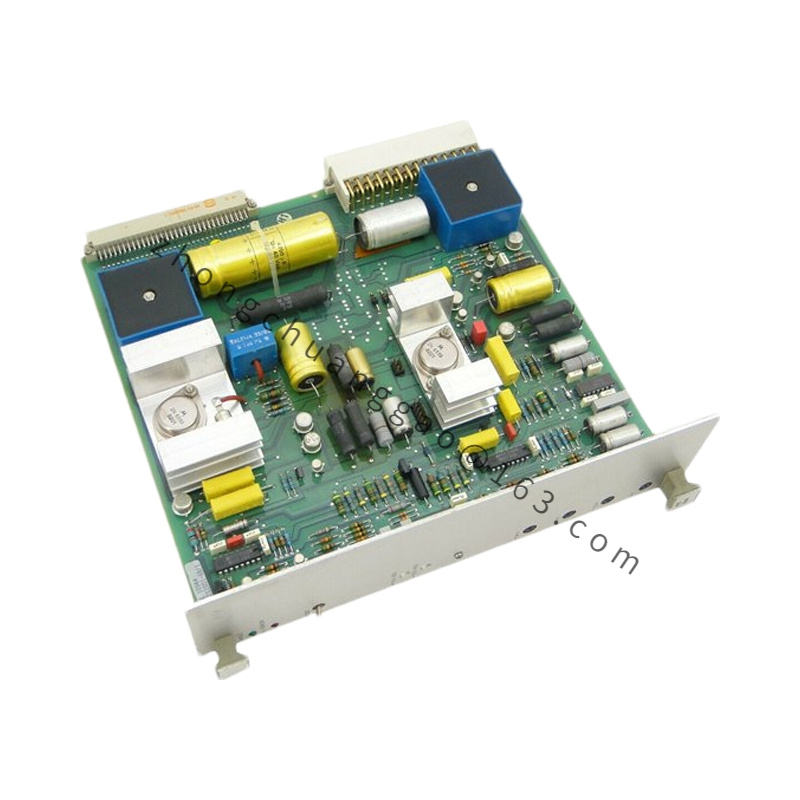
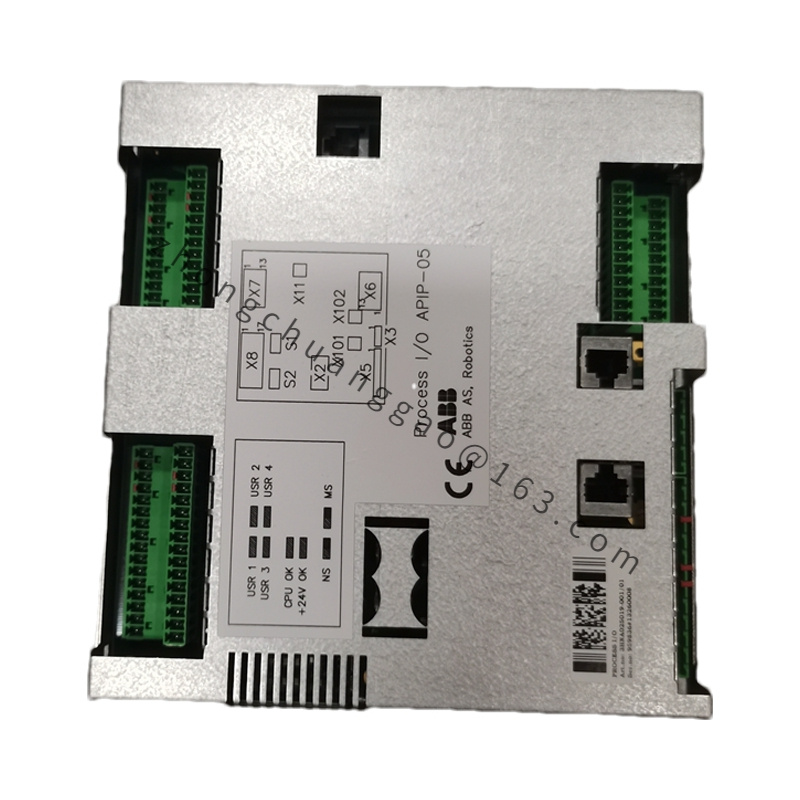
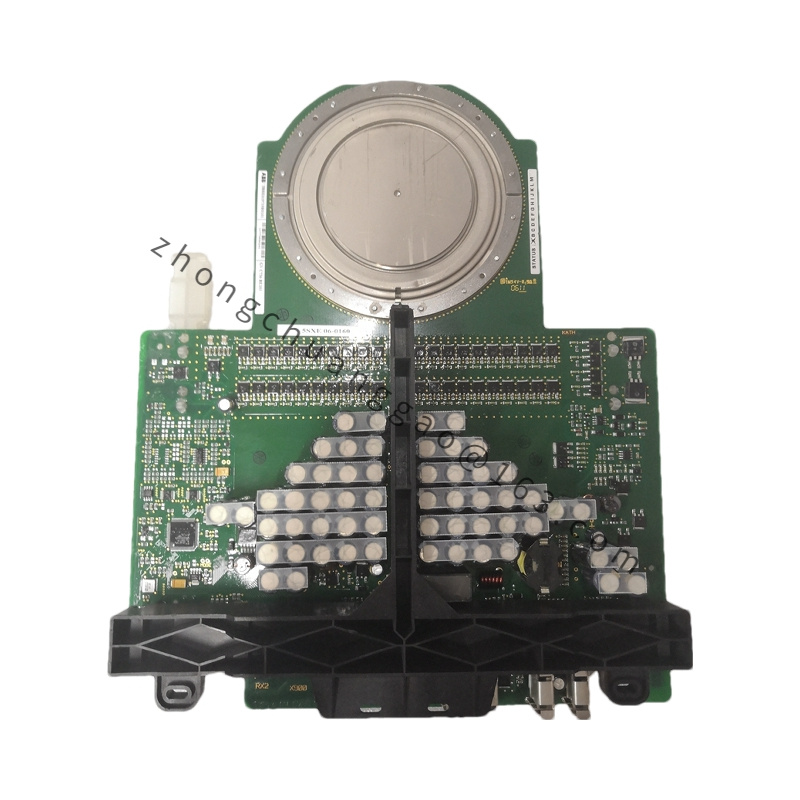
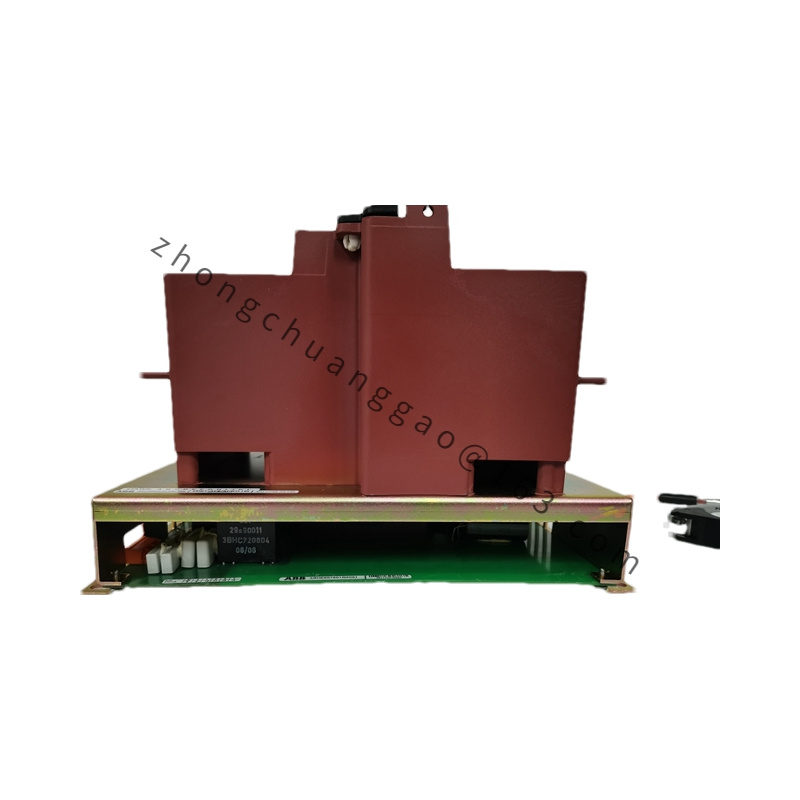
ABB UAD149A0011 3BHE014135R0011
Functional Features
- High Performance: Utilizes advanced digital signal processing technology for high-speed sampling and precise calculation, enabling high-precision position, speed, and force control.
- High Reliability: Ensures long-term stable operation through redundant design and high-quality materials and manufacturing processes.
- Flexibility: Supports multiple communication protocols and interfaces, facilitating easy integration with other devices or systems.
- Easy Programming and Use: Supports various programming languages and development tools for convenient secondary development and customization, along with a user-friendly operation interface and indicator lights.
- Low Power Consumption: Typical power consumption of only 2W, contributing to reduced overall system energy consumption.
- Rugged and Durable: Suitable for harsh environments, offering high durability and stability.
Detailed content
Technical Specifications
| Technical Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Model | ABB UAD149A0011 3BHE014135R0011 |
| Type | Universal Digital I/O Module / Servo Controller |
| Power Supply | 24V DC (Note: Depending on application, 220V may also be specified) |
| Power Consumption | 2W |
| I/O Points | 32 Points |
| I/O Type | Digital |
| I/O Signal | TTL Level |
| Scan Cycle | 25μs |
| Analog Accuracy | 12-bit (if applicable) |
| Digital Accuracy | 1-bit |
| Operating Temperature | -25°C to +70°C (Note: Depending on specification, +40°C may be mentioned for certain applications) |
| Storage Temperature | -40°C to +85°C |
| Protection Rating | IP67 (Note: IP68 may also be mentioned depending on model or application) |
| Dimensions | 145 mm x 100 mm x 45 mm |
| Weight | 2.59 kg |
| Material | Aluminum Alloy |
Application Scenarios
ABB UAD149A0011 3BHE014135R0011 is widely used in various industrial automation fields, including but not limited to:
- CNC Machines: For high-precision workpiece processing and motion control.
- Industrial Robots: Driving robot joints for precise movements and operations.
- Packaging Machinery: Controlling packaging equipment speed, position, and motion trajectories.
- Printing Equipment: Controlling various components of printing machines for high-quality printing operations.
- Material Handling: In logistics and warehousing, controlling conveyors, elevators, and other equipment for efficient material handling.
- Textile Machinery: Controlling textile machine movements and weaving operations.
- Medical Equipment: Such as surgical robots and CT scanners, for precise motion control.
- Automated Production Lines: Controlling motions and operations at different process steps.
- Laboratory Equipment: In research and laboratory settings, controlling experimental equipment motions and testing operations.








.jpg)