Detailed content
Technical Specifications
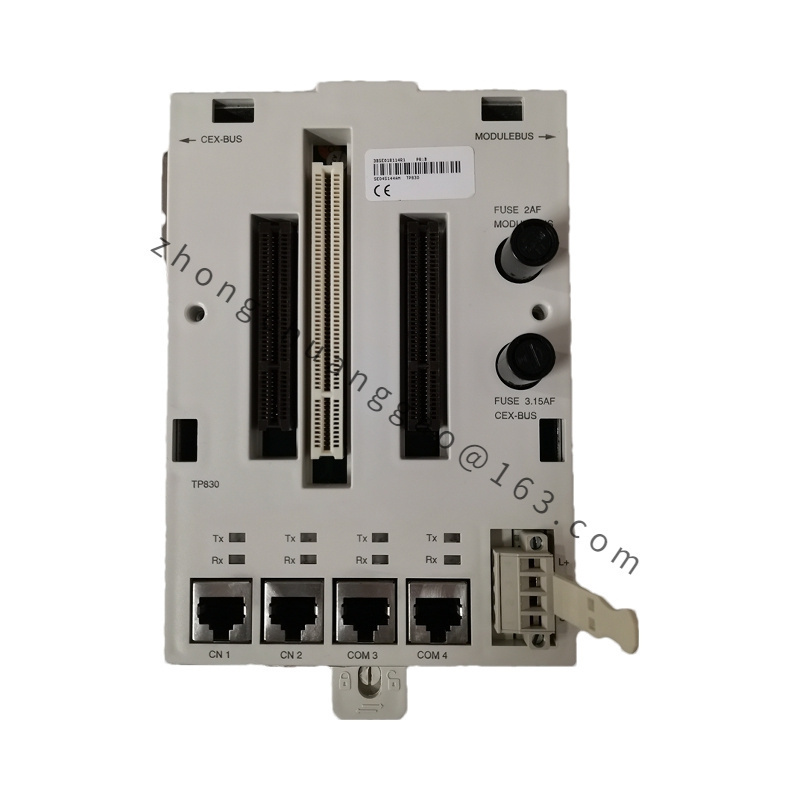
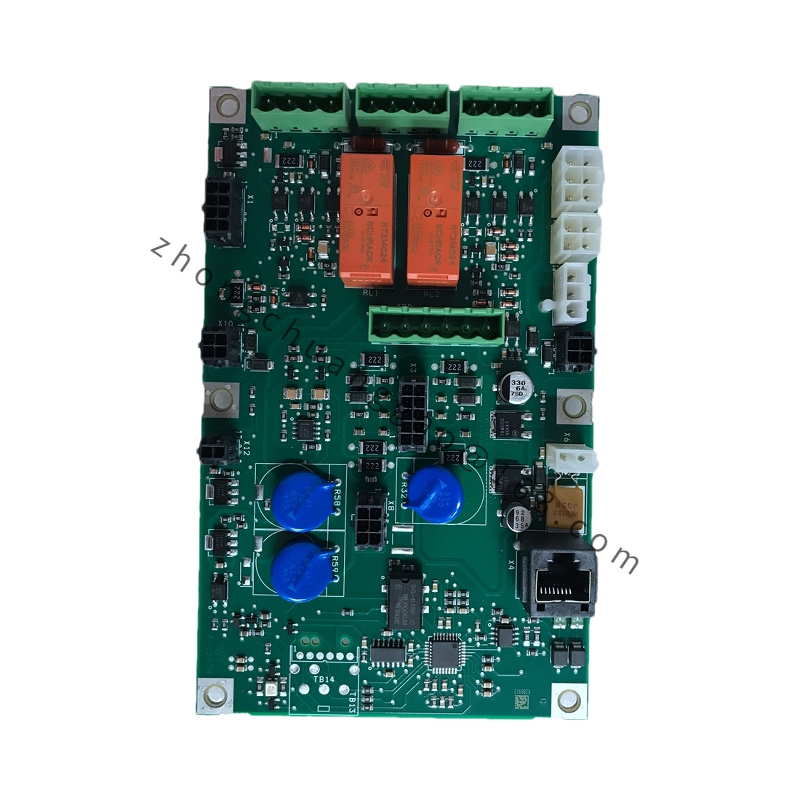
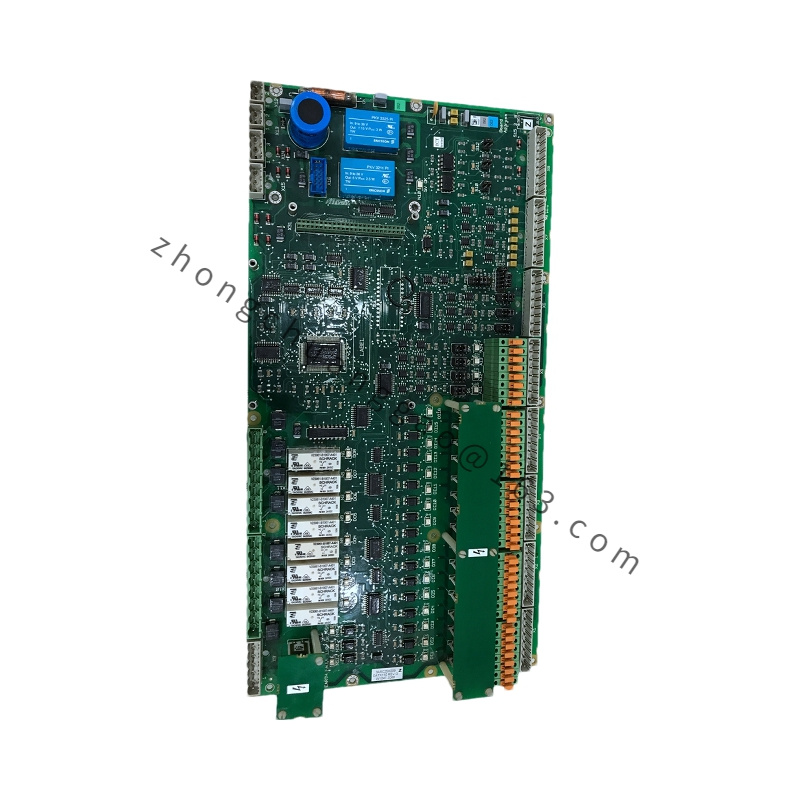
Module Type: Substrate module or processor module (depending on the variant, e.g., ABB TP830-1 is a processor module)
Processor: High-performance processor (in processor module variants, enabling fast data computation and processing)
I/O Interfaces:
Input/Output interfaces for connecting to sensors, actuators, and other external devices
May include digital input, digital output, analog input, and analog output interfaces
Communication Interfaces:
May support various communication protocols for connecting to other control devices or networks
Examples could include PLC-CAN communication modules for industrial networks
Power Requirements:
Modules typically require an appropriate power supply to function properly
Physical Characteristics:
Size and dimensions vary depending on the model and purpose
Designed to withstand industrial environments with factors such as vibration, temperature changes, and humidity
Functional Characteristics
Scalability:
Can be used together with other modules or substrates to achieve more complex control functions
Programmability:
Supports programmable control, allowing users to customize programming and algorithm development using specific programming languages or development tools
Real-Time Monitoring and Control:
Enables real-time monitoring and control of various industrial processes and equipment
Reliability and Stability:
Constructed with high-quality materials and manufacturing processes, ensuring reliability and stability
Can adapt to different working environment temperatures and humidity conditions
Ease of Use:
Supports plug-and-play functionality, facilitating installation and use
Simple and intuitive interfaces for operation
Application Scenarios
ABB TP830 is commonly used in various industrial automation and control applications, including but not limited to:
Process Control: For monitoring and controlling industrial processes such as chemical reactions, fermentation, and refining.
Manufacturing: Automation of production lines, robotic assembly, and machine control in manufacturing facilities.
Energy Management: Monitoring and controlling energy consumption, generation, and distribution in power plants and energy management systems.
Material Handling: Automation of conveyor belts, sorting systems, and storage facilities in warehouses and distribution centers.