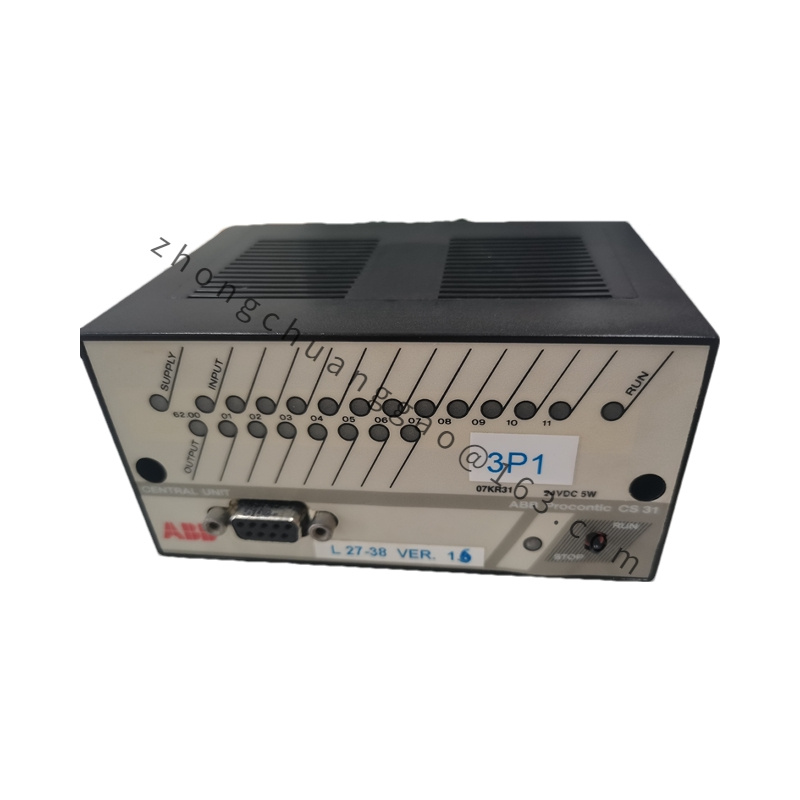
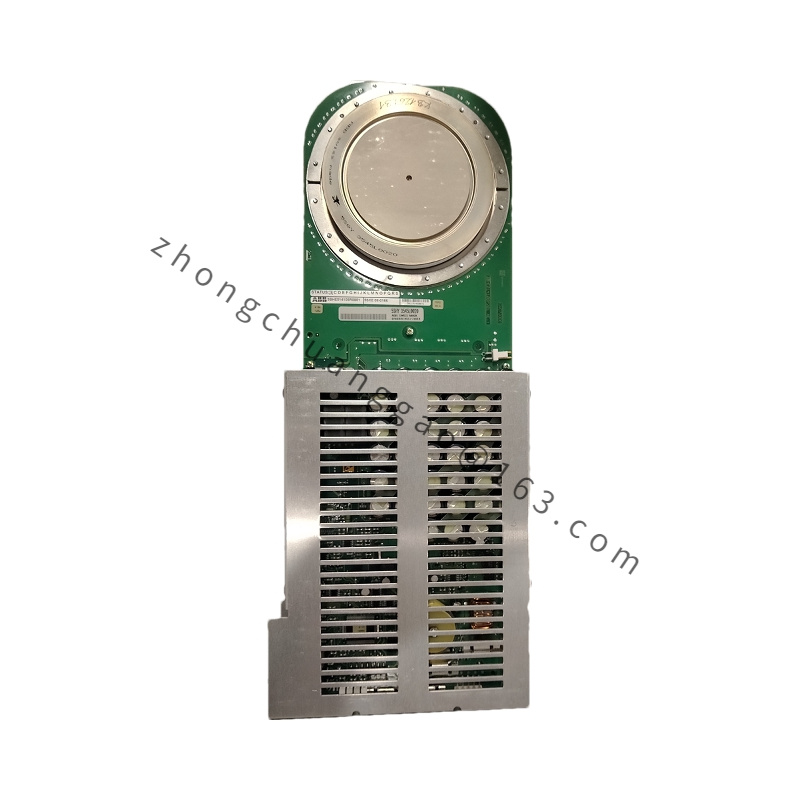
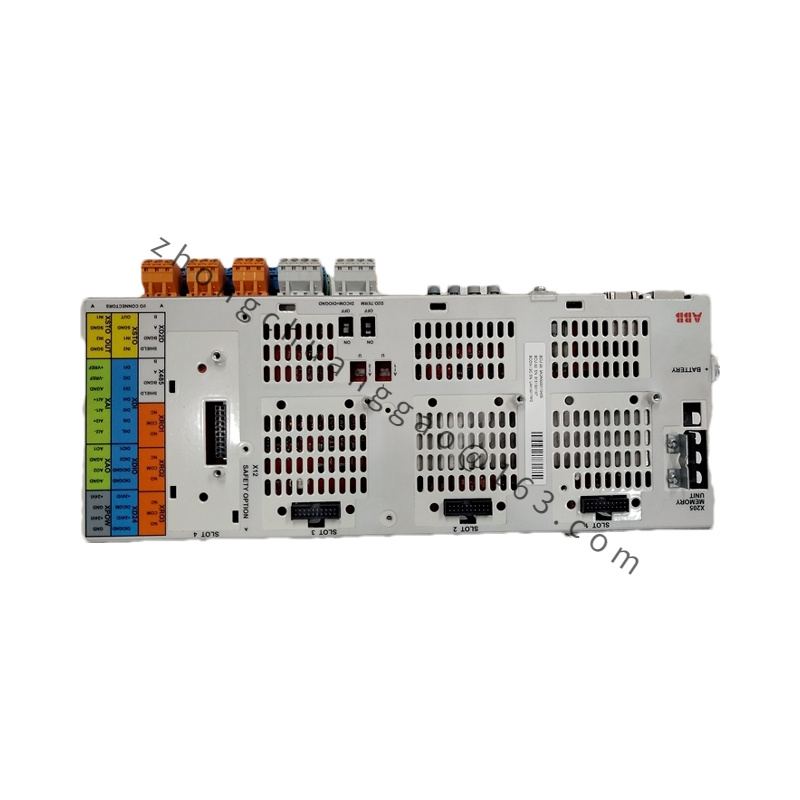
Detailed content
Technical Specifications
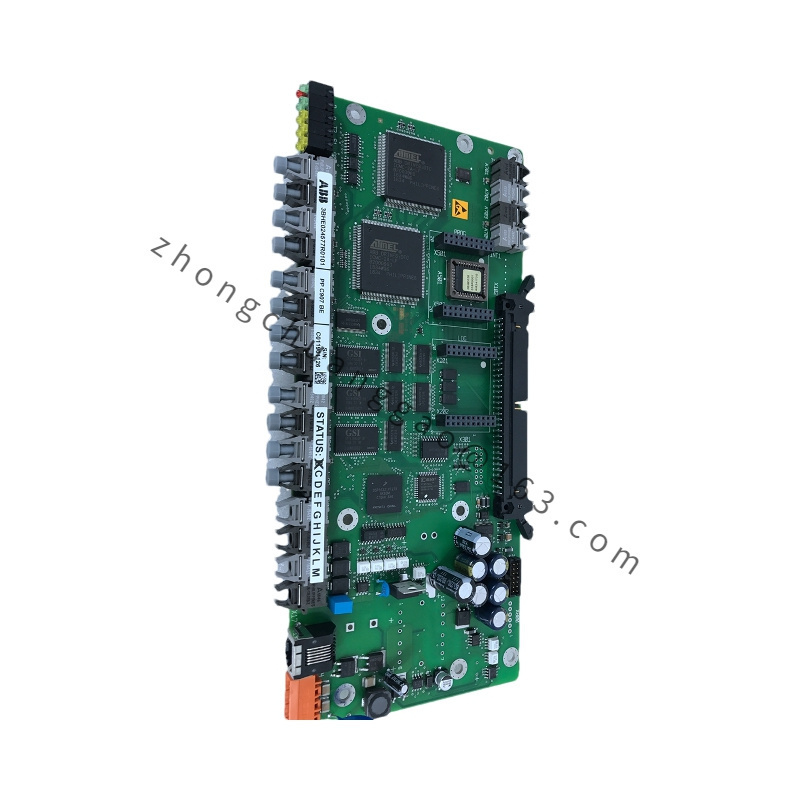
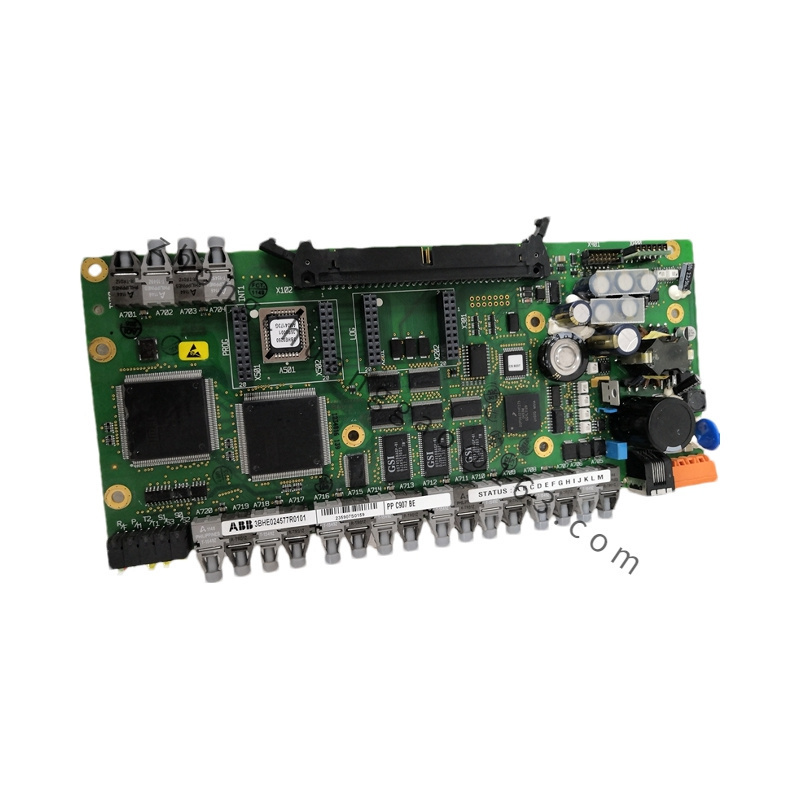
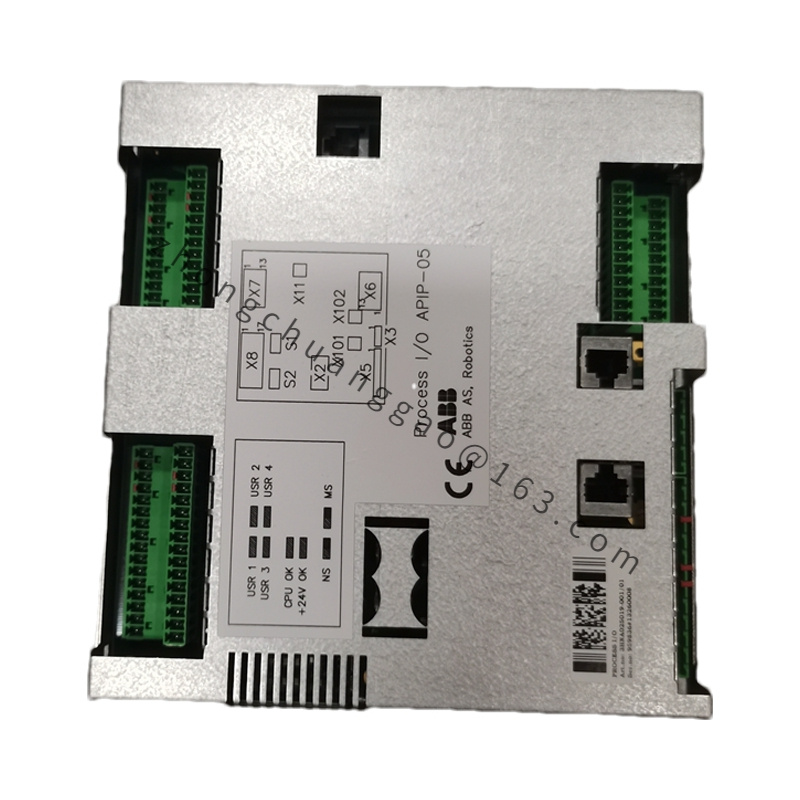
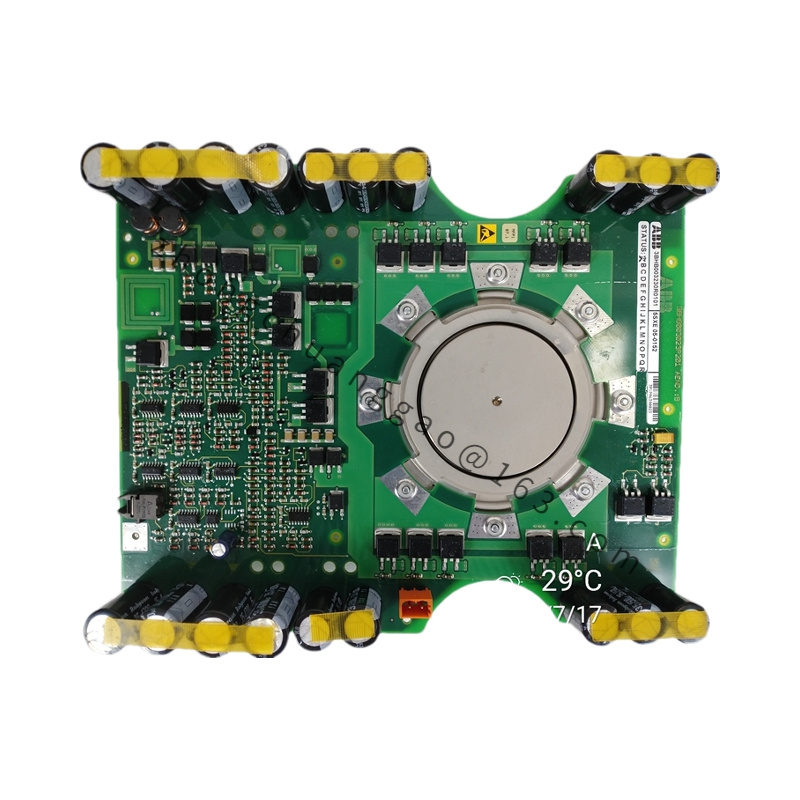
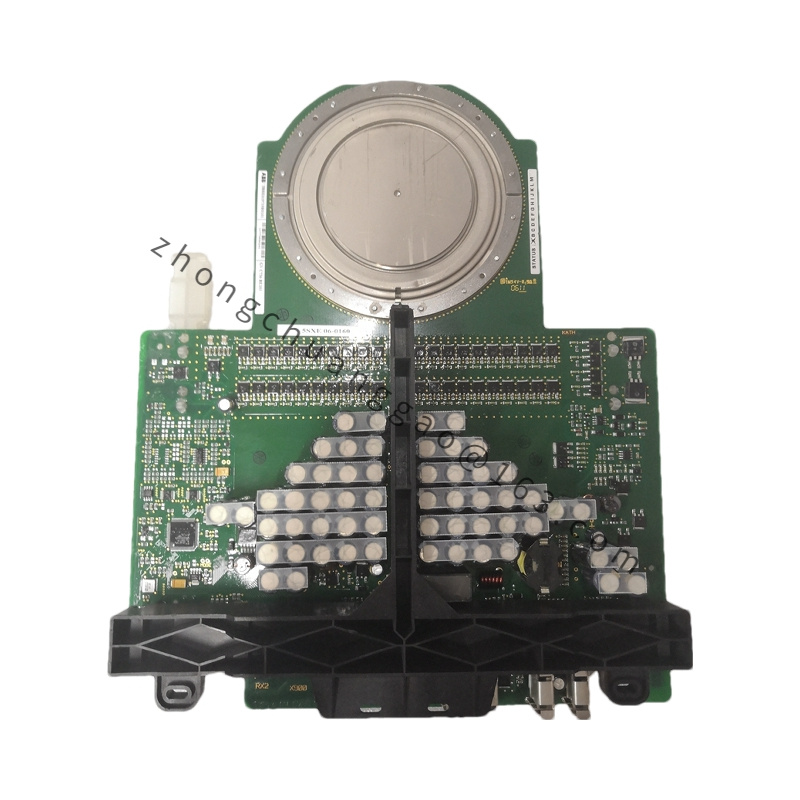
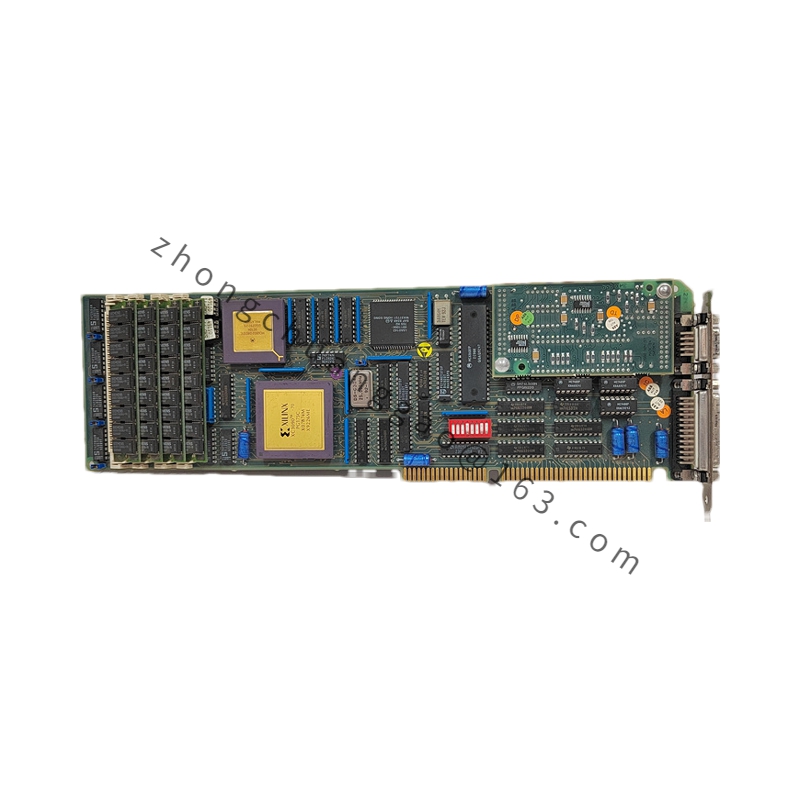
Model: PPC907BE (e.g., PPC907BE 3BHE024577R0101)
Weight: Approximately 1.7 kilograms
Input Voltage: DC 24V
Power Consumption: Maximum of approximately 4.5 watts
Input Signals: Digital or analog signals
Output Signals: Digital or analog signals
Operating Temperature: -40°C to +70°C
Protection Level: IP20
Functional Characteristics
High-Performance Processor: Equipped with a high-performance processor that enables efficient execution of complex control algorithms and operational tasks, meeting the demands of real-time control and data processing.
Multi-Core Architecture: Typically features a multi-core processor architecture, enhancing parallel processing capabilities and system response speed, allowing for simultaneous handling of multiple tasks and threads.
High Expandability and Flexibility: Designed with good expandability and flexibility, supporting multiple expansion slots for connecting additional modules and interfaces, enabling customization and enhancement of system functions and connectivity.
High Reliability and Stability: As part of ABB’s industrial automation portfolio, PPC907BE modules undergo rigorous quality control and testing to ensure reliable operation in industrial environments.
Communication Interfaces: Equipped with various communication interfaces, such as Ethernet, serial interfaces, and others, supporting communication protocols like Modbus, Profibus, and more, facilitating seamless data exchange and communication with other devices and systems.
Data Management and Processing: Capable of managing and storing large amounts of system data, including device status, process parameters, and fault information, and processing input data to output corresponding control signals.
High-Speed Data Transmission: Supports high-speed data transmission, enabling rapid transmission of large data volumes to meet the requirements of real-time control and data acquisition.
Application Scenarios
ABB PPC907BE modules are widely used in various industrial applications due to their high performance, reliability, and flexibility:
Industrial Automation: Utilized in automation control and monitoring systems for manufacturing, process control, and other industrial sectors.
Power Systems: Deployed in power generation, transmission, and distribution systems for control and protection, monitoring and regulating various power equipment parameters.
Mechanical Manufacturing: Employed in controlling various machine tools, machining centers, and other equipment, enabling high-precision and efficient processing.
Process Control: Suitable for applications in the chemical, pharmaceutical, food processing, and other process industries, where precise control of various processes is crucial.
Logistics Systems: Utilized in controlling automated warehouses, conveyor belts, robots, and other equipment, enhancing logistics efficiency and accuracy.
Data Centers: Can be used as a central server for managing data storage and access, providing efficient data processing and storage solutions.








.jpg)