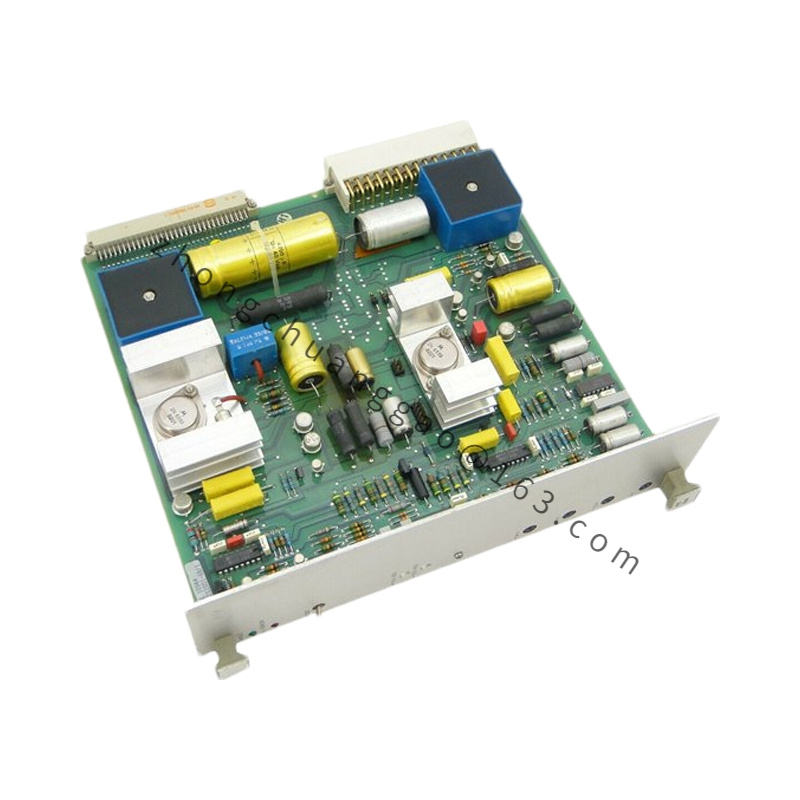
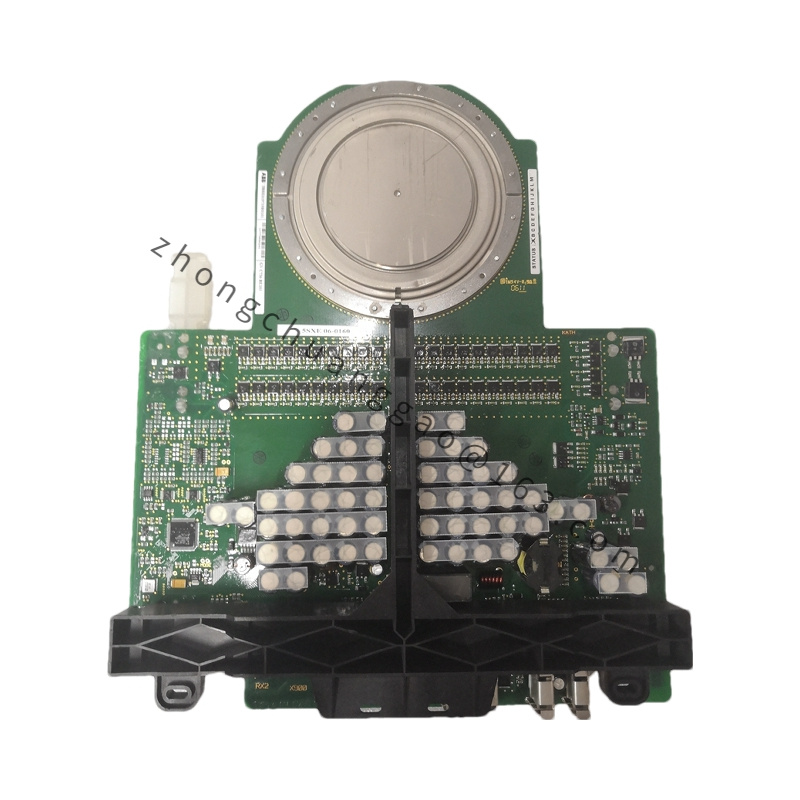
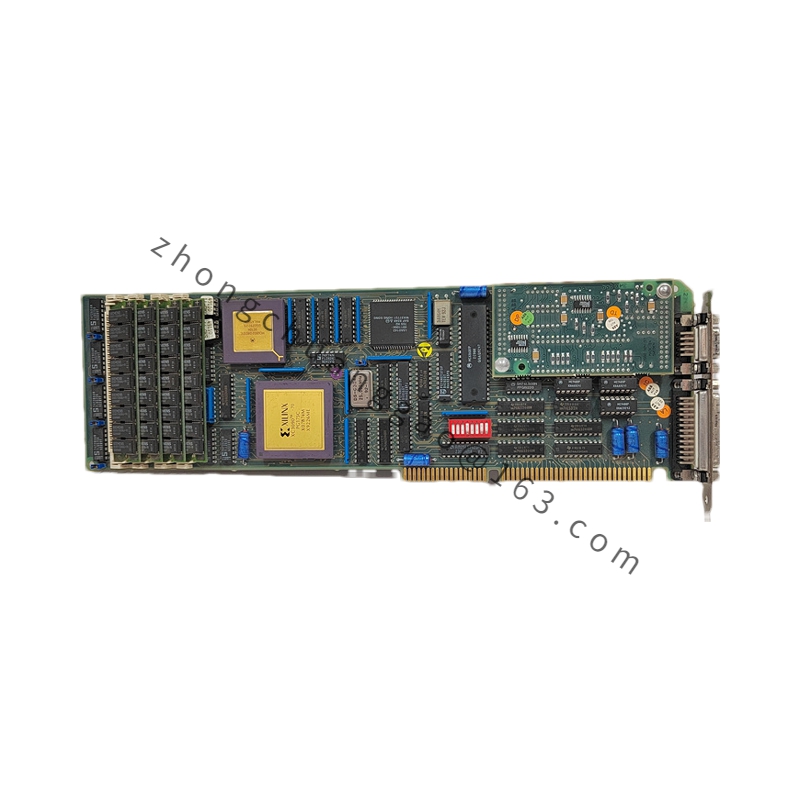
Detailed content
Technical Specifications
Processor: Equipped with a high-performance processor capable of executing various control algorithms and logical operations quickly.
Memory: Although specific memory capacities (e.g., RAM and flash memory) are not directly mentioned, ABB’s control system modules often include ample memory for efficient processing and data storage.
Communication Interfaces: The module is equipped with interfaces for communication with other control devices, supporting protocols such as Profibus DP, Modbus TCP/IP, and potentially others, enabling seamless integration and data transmission across systems.
Functional Characteristics
Core Processor Functions:
Handles input/output operations.
Executes control logic.
Communicates and monitors system status.
Programming and Logic Control:
Programmable according to specific application requirements, allowing for the implementation of control logic, alarms, and operations.
Supports standard IEC 61131-3 programming languages, including LD (Ladder Diagram), ST (Structured Text), FBD (Function Block Diagram), among others.
Communication Capabilities:
Enables integration with various devices through its diverse communication interfaces and protocols.
Facilitates system integration and data exchange between different components.
Safety and Reliability:
Known for its high safety and reliability standards, ensuring stable operation in industrial environments.
May include features like fault warning and self-diagnosis for ease of maintenance and reduced downtime.
Modular Design:
Allows for easy expansion and configuration based on specific application needs.
Enhances system flexibility and scalability.
Firmware and Software Support:
ABB typically provides firmware and software support to ensure the correct configuration and operation of the processor module.
Application Scenarios
ABB D674A906U01 automation processor module finds widespread application in various industries, including but not limited to:
Industrial Automation Systems: Utilized in automated production lines and processes for efficient control and monitoring.
Power Systems: Plays a crucial role in power distribution, management, and automation.
Manufacturing: Enhances production efficiency and quality control in various manufacturing settings.
Processing Plants: Used in chemical, food, and other processing plants for automated control and optimization.
Water Treatment: Assists in the automation of water treatment processes, ensuring efficient and safe water management.









.jpg)
.jpg)